Modern software needs to be updated quickly and reliably. Users expect new features, bug fixes, and security updates without delays or errors. CI/CD pipelines help development teams deliver software faster and with better quality — automatically.
What Is CI/CD?
CI/CD stands for:
- CI – Continuous Integration
- CD – Continuous Delivery or Continuous Deployment
Together, CI/CD is a set of automated processes that help developers build, test, and release software efficiently.
Continuous Integration (CI) Explained
Continuous Integration means developers regularly merge their code changes into a shared repository.
Every time code is added:
- The code is automatically built
- Automated tests are run
- Errors are detected early
Why CI Is Important
- Finds bugs early
- Reduces integration problems
- Ensures code works with the rest of the system
Instead of waiting until the end of a project to test everything, CI tests continuously.
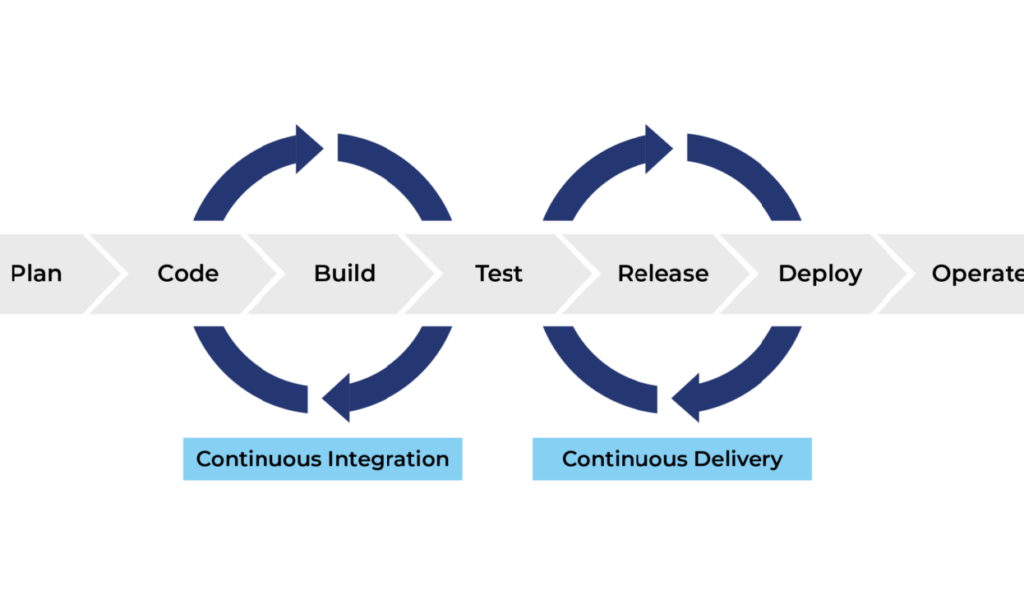
Continuous Delivery vs. Continuous Deployment
Continuous Delivery
Code is automatically tested and prepared for release, but a human decides when to deploy it to production.
Continuous Deployment
Every successful change is automatically deployed to production without manual approval.
Both approaches rely on automation — the difference is the final release step.
What Is a CI/CD Pipeline?
A CI/CD pipeline is a series of automated steps that code goes through from development to production.
Think of it like an assembly line for software.
Typical CI/CD Pipeline Stages
- Code Commit – Developer pushes code
- Build – Application is compiled
- Test – Automated tests are run
- Security Checks – Vulnerabilities are scanned
- Deploy – Application is released
If any step fails, the pipeline stops and alerts the team.
Why CI/CD Pipelines Matter
CI/CD pipelines provide many benefits:
- 🚀 Faster software releases
- 🐞 Fewer bugs in production
- 🔁 Consistent and repeatable deployments
- 🤝 Better collaboration between teams
- 🔐 Improved security through automated checks
Common CI/CD Tools
Popular CI/CD tools include:
- Jenkins
- GitHub Actions
- GitLab CI/CD
- CircleCI
- Azure DevOps
These tools connect with code repositories and automate pipeline steps.
CI/CD in Simple Terms
Without CI/CD:
Developers manually test and deploy code, which is slow and error-prone.
With CI/CD:
Software updates flow automatically from code to production, safely and quickly.
Challenges of CI/CD
- Initial setup can be complex
- Requires good automated tests
- Teams must maintain pipelines regularly
However, the long-term benefits far outweigh these challenges.
The Future of CI/CD
CI/CD pipelines are evolving with:
- Cloud-native platforms
- Containerization (Docker, Kubernetes)
- AI-driven testing and monitoring
These advancements make pipelines faster, smarter, and more reliable.
Conclusion
CI/CD pipelines are essential for modern software development. By automating integration, testing, and deployment, they help teams deliver high-quality software at speed.
Simply put, CI/CD pipelines turn software development into a smooth, automated process instead of a risky manual one.