The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a structured process used by organizations to design, develop, test, and maintain software efficiently. It provides a systematic approach that ensures software is high-quality, delivered on time, and meets user requirements.
What Is SDLC?
SDLC stands for Software Development Life Cycle.
It defines a series of phases that guide the development of software from initial idea to final deployment and maintenance.
The main goal of SDLC is to produce reliable, scalable, and secure software while minimizing risks and development costs.
Why Is SDLC Important?
SDLC helps teams:
- Plan projects effectively
- Reduce development risks
- Improve software quality
- Manage time and costs
- Ensure customer satisfaction
Without a defined SDLC, software projects are more likely to face delays, budget overruns, and technical issues.
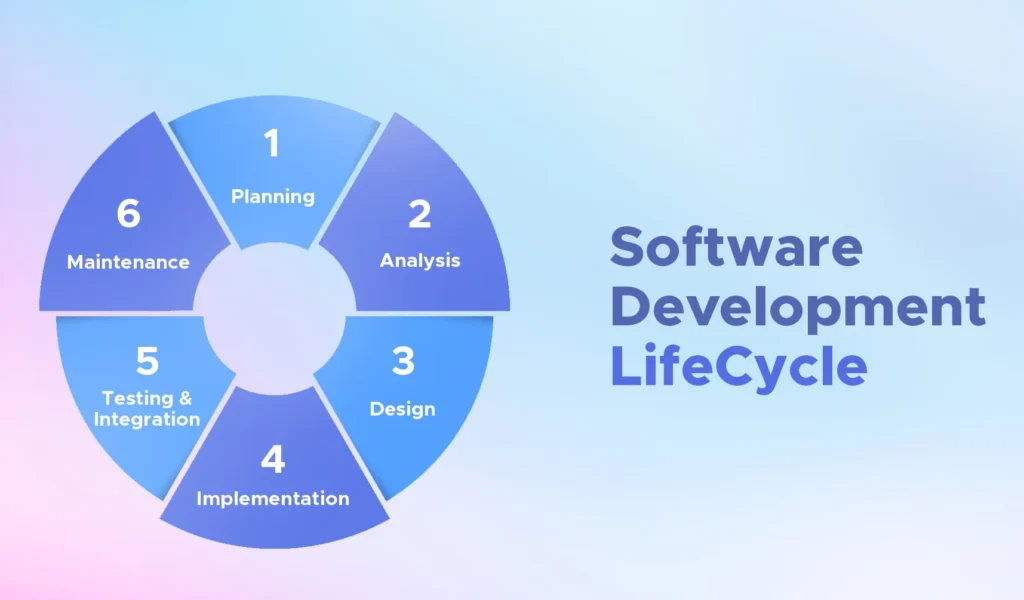
Phases of the Software Development Life Cycle
1. Requirement Analysis
This is the first phase where stakeholders and developers gather and analyze requirements.
Key Activities:
- Understanding user needs
- Defining functional and non-functional requirements
- Creating requirement documents
This phase ensures everyone agrees on what the software should do.
2. System Design
In this phase, the overall system architecture is planned.
Key Activities:
- Designing system architecture
- Choosing technologies and tools
- Creating database and interface designs
A strong design helps reduce future development problems.
3. Implementation (Development)
This is where developers start writing code based on the design.
Key Activities:
- Writing source code
- Following coding standards
- Performing unit testing
This phase transforms design documents into a working software product.
4. Testing
The software is tested to ensure it works as expected and is free of defects.
Key Activities:
- Functional testing
- Performance testing
- Security testing
- Bug fixing
Testing ensures the software meets quality standards before release.
5. Deployment
Once testing is successful, the software is deployed to the production environment.
Key Activities:
- Installing software
- Configuring systems
- Releasing to users
Deployment can be done in stages or all at once, depending on the project.
6. Maintenance
After deployment, ongoing support and improvements are provided.
Key Activities:
- Fixing bugs
- Updating features
- Improving performance
- Ensuring security
This phase continues throughout the software’s life.
Popular SDLC Models
Different projects use different SDLC models:
- Waterfall Model: Linear and sequential
- Agile Model: Iterative and flexible
- Spiral Model: Risk-focused and iterative
- V-Model: Emphasizes testing
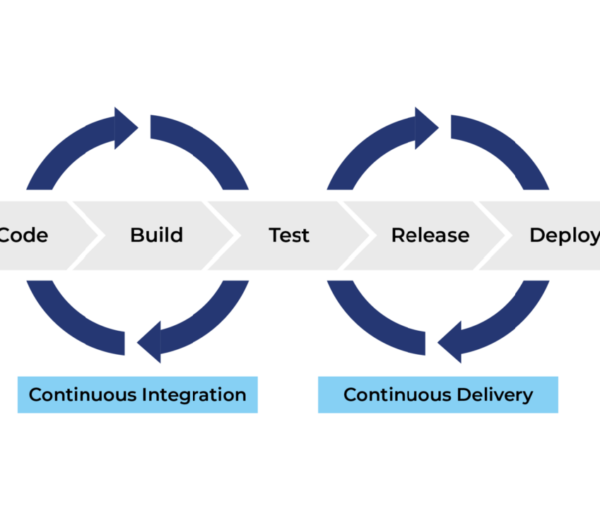
- DevOps Model: Combines development and operations
Each model has its own advantages based on project needs.
Advantages of Using SDLC
- Clear project structure
- Better documentation
- Improved quality control
- Reduced risks
- Predictable outcomes
Challenges of SDLC
- Can be time-consuming
- Requires detailed planning
- Less flexibility in traditional models
Modern approaches like Agile and DevOps help overcome many of these challenges.
SDLC in Simple Terms
SDLC is like building a house:
- Plan the house
- Design it
- Build it
- Inspect it
- Move in
- Maintain it
Skipping any step can cause problems later.
Conclusion
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) provides a clear framework for developing high-quality software. By following its phases and choosing the right model, organizations can deliver software that meets user expectations while controlling time, cost, and risk.
Simply put, SDLC turns ideas into reliable software through a structured and organized process.